Informaçao geral
Directorios
Textos
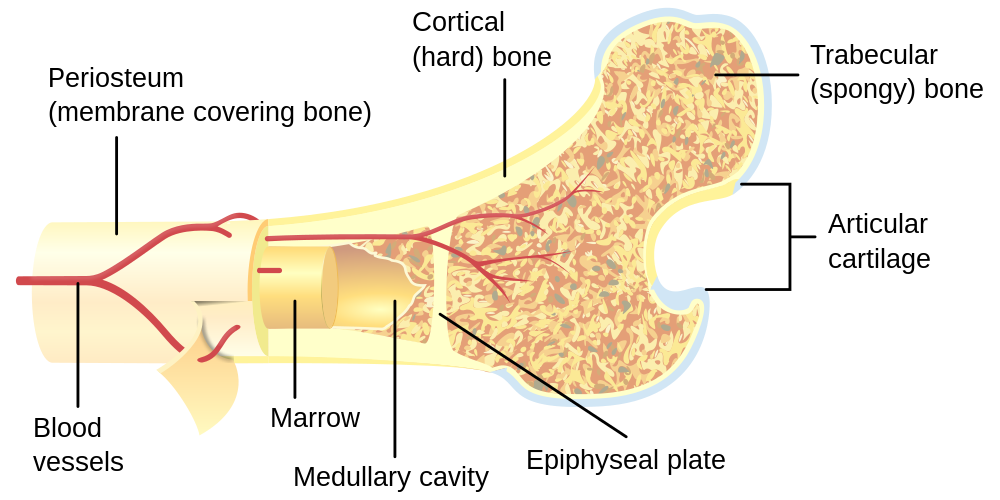
Celulas osseas


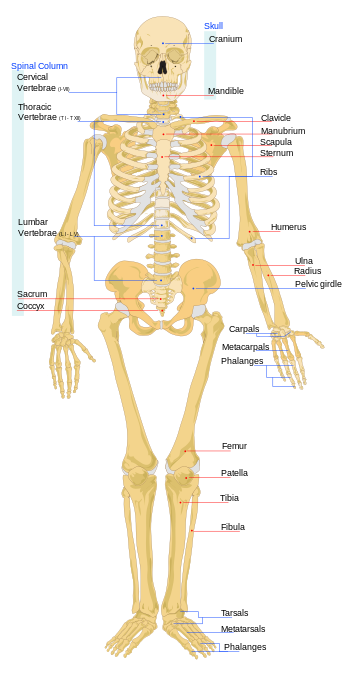
Estrutura óssea
Ossos compactos
http://www.dbriers.com/tutorials/2012/12/difference-between-compact-bone-and-spongy-bone-simplified/
| Compact Bone | Spongy Bone |
| Made up of osteons | Made up of trabeculae |
| Calcium is present in high quantity in them | Very small amount of calcium is present in them |
| Almost 80% or above weight of human skeleton is contributed by compact bones | The rest 20% weight of the skeleton is contributed by spongy bones |
| These bones are cylindrical in shape | These are cuboidal in shape |
| These contain yellow marrow | These mostly contain red bone marrow |
| Compact bones form major part of human body’s long bones. For e.g. arms, legs, etc. | Spongy bones form major part of our short bones. For e.g. ankles or wris |
Ossos esponjosos ( cancellous)
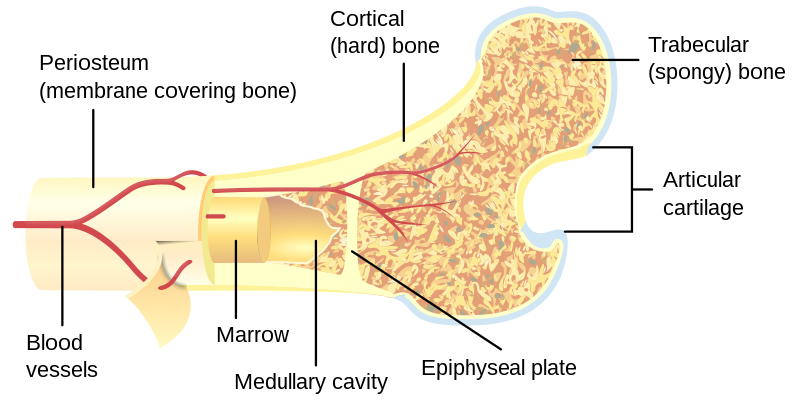
Fisiologia óssea

Ossificaçao

Remodelaçao óssea

1. Activation: preosteoclasts are stimulated and differentiate under the influence of cytokines and growth factors into mature active osteoclasts
2. Resorption: osteoclasts digest mineral matrix (old bone)
3. Reversal: end of resorption
4. Formation: osteoblasts synthesize new bone matrix
5. Quiescence: osteoblasts become resting bone lining cells on the newly formed bone surface
https://courses.washington.edu/bonephys/physremod.html
2. Resorption: osteoclasts digest mineral matrix (old bone)
3. Reversal: end of resorption
4. Formation: osteoblasts synthesize new bone matrix
5. Quiescence: osteoblasts become resting bone lining cells on the newly formed bone surface
https://courses.washington.edu/bonephys/physremod.html
Informaçao especializada
Acondrogenese
 The appearance of the female baby with achondrogenesis type I after birth. Baby weighed 1810 grams and measured 31 centimeters; died within the first thirty minutes of birth.
The appearance of the female baby with achondrogenesis type I after birth. Baby weighed 1810 grams and measured 31 centimeters; died within the first thirty minutes of birth.
Acondroplasia
Acrocefalosindactilia
Ver:
· Apert ( acrosindactilia tipo 1)
· Crouzon( tipo 2)
· Saethre Chotzen ( tipo 4)
· Pfeiffer/ tipo 5)
Acrocefalopolidactilia
Ver:
· Noack ( tipo1)
· Carpenter ( tipo 2)
· Sakati–Nyhan–Tisdale ( tipo 3)
· Pfeiffer ( tipo 5)
Acrodisostose
Acromegalia
Acroosteolise
Algodistrofia
Antley- Bixler
Apert
Aqueiropodia
Artrogripose
Atelosteogenese
Tipo 1
Tipo 2
Tipo 3
Calcifilaxia
Camurati - Engelman
Carpenter
Cancro dos ossos
Condrocalcinose
Condrodisplasia
Conradi-Hunerman
Condrosarcoma
Cordoma
Crouzon

Diferenças no comprimento das pernas
Depositos de pirofosfato de cálcio nos ossos
Discondrosteose
Discondroplasia
Disostose craneofacial
Ver CROUZON
Displasias
Ehler- Danlos
Ellis van Crevelt

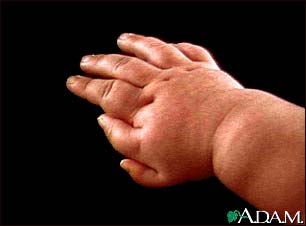

Encondromatose
Fibrocondrogenese
Fibroplasia ossificante progressiva
 The effects of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, a disease which causes damaged soft tissue to regrow as bone. Sufferers are slowly imprisoned by their own skeletons.
The effects of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, a disease which causes damaged soft tissue to regrow as bone. Sufferers are slowly imprisoned by their own skeletons.
Focomielia
Fluorose esquelética
Gorham
Hiperostose cortical infantil( Caffey(
Hipocondrogenese
Hipofosfatasia
Jarco- Levin
Klippel- Feil
Kniest
Legg- Calve. Perthes
Maffuci
Marfan
Meloreostose
Moebius
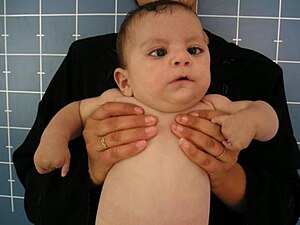 A child with oromandibular-limb hypogenesis-Möbius syndrome. Notice the expressionless face (due to bilateral VII nerve palsies) and missing fingers
A child with oromandibular-limb hypogenesis-Möbius syndrome. Notice the expressionless face (due to bilateral VII nerve palsies) and missing fingers
Necrose avascular
Noack
É uma variante do Sindroma de Pfeiffer
Ollier
Ver Encondromatose
Ortotica
Osgood- Schlater
In Osgood-Schlatter disease, the enlarged, inflamed tibial tubercle is nearly always tender when pressure is applied.
http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osgood-schlatter-disease/basics/definition/con-20021911
Osteites
Osteoartrites
Osteocondrite dissecante
Osteocondrite do calcanhar
Osteocondromatose (exostose múltipla hereditária)
Osteofitos
Osteogenese imperfeita
Osteolise da clavícula distal
Osteomielite
Osteoma coroideu

Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia oncogénica
Osteonecrose
Osteopenia
Osteosarcomas
Paget do osso
Pfeiffer
Raquitismo
Saethre-Crotzen
Sakati–Nyhan–Tisdale
Sindroma oculodentodigital
Sindroma otopalatodigital
Transplantes osseos
http://my.clevelandclinic.org/services/orthopaedics-rheumatology/treatments-procedures/bone-grafting
Outras doenças dos ossos
Discondroplasia ( Ollier)
Displasia cleidocraneana
Genetica
Displasia boomerang
Genetica
Displasia campomelica
Genetica
Displasia craneodiafisaria
Displasia craneometafisaria
Genetica
Displasia de Czech
Genetica
Displasia diastrófica
Genetica
Displasia epifisária
Genetica
Tratamento
Displasia esquelética letal
Genetica
Tipos
Displasia fibrosa do osso
Ver tumores dos ossos
Displasia de Kniest
Displasia de Kniest
Displasia mesomelica
Displasia
Fasceites
Fasceite necrotizante
Fasceite plantar
Fibrocondrogenese
Gorham
Hiperostose cortical infantil (Caffey)
Hipocondrogenese
Maffucci
Meloreostose
Onicolise
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319851.php?utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=daily-hcp
Osteite fibrosa quistica
Osteite do pubis
Osteocondromatose
Osteogenese imperfeita
Directorios
Textos
Osteomielite
Osteomielite multifocal trcorrente
Osteopenia
Osteopetrose
Paget do osso
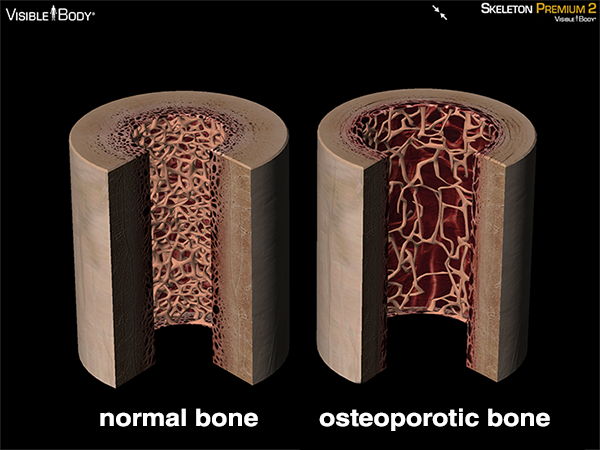
Osteoporose
TUMORES DOS OSSOS
Directorios
Textos
Tratamento
TUMORES DOS OSSOS
Tumores benignos
Cancro primário do osso
Estadios
http://www.macmillan.org.uk/Cancerinformation/Cancertypes/Bone/Symptomsdiagnosis/Gradingstaging.aspx
Tipos de cancro
Condroma
Condrosarcoma
Displasia fibrosa do osso
Tratamento
Ewing
Directorios
Textos
Fibroma condromixoide
Fibroma não ossificante
Metastases osseas
Osteocondroma
Osteosarcoma
Tumores de células gigantes do osso
Tratamento
ARTICULAÇÕES
Informações gerais
Directorios
Textos
Envelhecimento das articulações
Tipos de articulações
Directorios
Textos
Animações
PATOLOGIA ARTICULAR
Artrografia
Artrogripose
Artrogripose e displasia ectodérmica
Artrogripose distal
Tipos
Tipo 2b (Sheldon- Hall)
Tipo 2 A (Freeman- Sheldon)
Tipo 1A
Genetica
Artogripose multiplex congenita
Artroses
Artrite reumatóide
Bursites
Condrodistrofia
Condrosarcoma
Displasia metatropica
Entorses e estiramentos
Estiramentos repetitivos
Espondilartrite anquilosante
Estalidos nas articulações
Fasceites
Gota
Hipermobilidade articular
Sarcomas sinoviais
Tendinites
Tenosinovite
Tietze
Transplantes dos ossos
Reiter